Difference between revisions of "Sound source localization for robots"
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
|number=1 | |number=1 | ||
|cfu=20 | |cfu=20 | ||
| − | |image= | + | |image=TESI.png |
}} | }} | ||
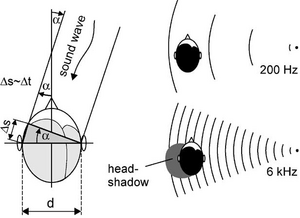
Analysis of the state-of-the-art of sound source localisation algorithms. Application and improvement of existing systems developping a binaural models to apply on a robot, initially based on a stereo acquisition, then using different type of sensors (microphone array, MEMS, etc...). | Analysis of the state-of-the-art of sound source localisation algorithms. Application and improvement of existing systems developping a binaural models to apply on a robot, initially based on a stereo acquisition, then using different type of sensors (microphone array, MEMS, etc...). | ||
Revision as of 11:22, 10 December 2015
| Title: | Sound source localization for robots | |
|---|---|---|
| Description: | Analysis of the state-of-the-art of binaural systems for audio detection and localization in robotics | |
| Tutor: | MatteoMatteucci | |
| Start: | 2015/10/08 | |
| Number of students: | 1 | |
| CFU: | 20 |
Analysis of the state-of-the-art of sound source localisation algorithms. Application and improvement of existing systems developping a binaural models to apply on a robot, initially based on a stereo acquisition, then using different type of sensors (microphone array, MEMS, etc...).
Essential bibliography:
Haykin, Simon, and Zhe Chen. "The cocktail party problem." Neural computation 17.9 (2005): 1875-1902 [1]
Deleforge, Antoine, and Radu Horaud. "The cocktail party robot: Sound source separation and localisation with an active binaural head." Proceedings of the seventh annual ACM/IEEE international conference on Human-Robot Interaction. ACM, 2012. [2]
Antoine Deleforge, Radu Horaud, Yoav Y. Schechner, Laurent Girin. Co-Localization of Audio Sources in Images Using Binaural Features and Locally- Linear Regression. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech and Language Pro-cessing, Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), 2015, 23 (4), pp.718-731. [3]
Schwarz, Andreas, and Walter Kellermann. "Coherent-to-Diffuse Power Ratio Estimation for Dereverberation." Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, IEEE/ACM Transactions on 23.6 (2015): 1006-1018. [4] Willert, Volker, et al. "A probabilistic model for binaural sound localization." Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part B: Cybernetics, IEEE Transactions on 36.5 (2006): 982-994. [5]
Lu, Yan-Chen, and Martin Cooke. "Binaural estimation of sound source distance via the direct-to-reverberant energy ratio for static and moving sources." Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, IEEE Transactions on 18.7 (2010): 1793-1805. [6]
Deleforge, Antoine, and Radu Horaud. "Learning the direction of a sound source using head motions and spectral features." (2011): 29. [7]
Le Roux, Jonathan, and Emmanuel Vincent. "A categorization of robust speech processing datasets." (2014). [8]