Difference between revisions of "Robot development"
m |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | [[Category:Research Topic]] | ||
| + | |||
We are developing robots since 1971, as tools for research and applications. Among the last ones, we mention the autonomous wheelchair LURCH, the team of soccer robots Milan Robocup Team, and several bio inspired robots. | We are developing robots since 1971, as tools for research and applications. Among the last ones, we mention the autonomous wheelchair LURCH, the team of soccer robots Milan Robocup Team, and several bio inspired robots. | ||
Revision as of 18:41, 25 October 2009
We are developing robots since 1971, as tools for research and applications. Among the last ones, we mention the autonomous wheelchair LURCH, the team of soccer robots Milan Robocup Team, and several bio inspired robots.
Projects
Projects on this topic:
- AGW (AGW - Automatic Guided Wheelchair)
- Adaptive Behaviors for Robogames (Adaptive Behaviors for Robogames)
- Adaptive Predicates (Adaptive Predicates)
- Affective Robot force sensor (Affective Robot force sensor)
- Autonomous Robot for emotional interaction (Autonomous Robot for emotional interaction)
- Balancing robots: Tilty, TiltOne (BalancingRobots)
- Ballbot (Ballbot)
- C-SLAM (C-SLAM)
- Cestino (Cestino)
- Concierge (Concierge)
- CrickBot (CrickBot)
- Crocobot (Crocobot)
- DiffDrivePlanner (Search-based Differential Drive Planner)
- E-2? - A robot for exhibitions (E-2? - A robot for exhibitions)
- E-2? Behaviors (E-2? Behaviors)
- E-2? Body (E-2? Body)
- E2GoHome (E2GoHome)
- EKF on Manifolds (EKF on Manifolds)
- EMBOT (EMBOT)
- Emotional Bioinspired Control (Emotional Bioinspired Control)
- … further results
Project proposals
| Wiki Page: | Barking Robots | |
| Title: | Barking Robots | |
| Description: | Aim of this project is the development of a robot that can operate autonomously at exhibitions and malls to attract people to a given location, by showing interesting behaviors and interacting with people.
The robot first exhibition has been at Robotica 2009, within HI-Tech Expo at Fiera di Milano, on November 23-25, 2009. Here, the robot had to go around in an area delimited by a white stripe and contact verbally and with gestures people entering the area, in order to attract them to the booth. Behaviors and gestures have still to be developed to come to an interesting and robust demo at next Robotica, or at other ehibits (e.g. at the Museo della Scienza of Milan). | |
| Tutor: | [[AndreaBonarini | ]] (, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , … further resultswarning.png
| |
| Start: | 25 February 2012 | |
| Students: | 1 - 2 | |
| CFU: | 5 - 20 | |
| Research Area: | Robotics | |
| Research Topic: | Robot development | |
| Level: | Bachelor of Science, Master of Science | |
| Type: | Thesis |
| Wiki Page: | CAN Bus bootloader for STM32 microcontrollers | |
| Title: | CAN Bus bootloader for STM32 microcontrollers | |
| Description: | JOINT PROJECT with the Embedded Systems group (contact: Patrick Bellasi http://home.dei.polimi.it/bellasi/)
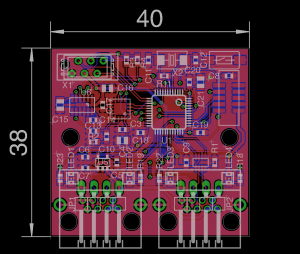
In order to speed up the development and the maintenance of embedded applications, a way to update the firmware on a microcontroller without the need of connecting cables or programmers can be very handy. We are developing a framework for rapid prototyping of low-cost robots, with smart devices that exchange data on a CAN bus network. The CAN bus bootloader is one of the components we need for this project, enabling remote firmware upgrades of all the devices connected to the CAN network. This project aims to develop a CAN bus bootloader for STM32 ARM Cortex-M3 microcontrollers, and eventually for other architectures. | |
| Tutor: | [[AndreaBonarini | ]] (, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , … further resultswarning.png
| |
| Start: | 1 March 2012 | |
| Students: | 1 - 2 | |
| CFU: | 2 - 5 | |
| Research Area: | Robotics | |
| Research Topic: | Robot development | |
| Level: | Bachelor of Science, Master of Science | |
| Type: | Course |
| Wiki Page: | Embedded registers view plug-in for Eclipse | |
| Title: | Embedded registers view plug-in for Eclipse | |
| Description: | JOINT PROJECT with the Embedded Systems group (contact: Patrick Bellasi http://home.dei.polimi.it/bellasi/)
When developing embedded applications it is frequently needed to look at *hardware register content* in order to *debug the code*. All commercial development suites offer register views that show their contents as well as the meaning of each bit. Open source development solutions currently lack this feature, meaning that you have to look to the correct memory location and map the content to the corresponding register bits manually. This seems to be one of the most limiting issues when developing embedded application using open source solutions. This project aims to fill this gap, developing an Eclipse plug-in that shows the register contents in a tree viewer, like most commercial suites do. | |
| Tutor: | [[AndreaBonarini | ]] (, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , … further resultswarning.png
| |
| Start: | 30 May 2011 | |
| Students: | 1 - 2 | |
| CFU: | 2 - 5 | |
| Research Area: | Robotics | |
| Research Topic: | Robot development | |
| Level: | Bachelor of Science, Master of Science | |
| Type: | Course |
| Wiki Page: | LCM middleware on embedded platform | |
| Title: | LCM middleware on embedded platform | |
| Description: | We are developing a framework for rapid prototyping of low-cost robotic systems. To fasten robot design and building, and to make software and hardware reuse easier, a modular architecture is mandatory.
In a context of smart modules that have to cooperate by exchanging data to reach their common goal, the communication protocol and middleware are core components. This project is about the middleware component, a publish/subscribe system that takes care of managing topics, publisher and subscribers, and of marshaling data before sending it. This project aims at porting the LCM marshaling and middleware library, developed at MIT and used in the Grand Challenge competition, to embedded systems, in order to exploit the existing LCM tools and to be compliant with an existing and efficient technology. The project consists in:
The projects has to be developed in ANSI C, and experience with embedded platforms is a plus. | |
| Tutor: | [[AndreaBonarini | ]] (, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , … further resultswarning.png
| |
| Start: | 1 October 2011 | |
| Students: | 1 - 2 | |
| CFU: | 20 - 20 | |
| Research Area: | Robotics | |
| Research Topic: | Robot development | |
| Level: | Master of Science | |
| Type: | Thesis |
| Wiki Page: | Odometric system for robots based on laser mice | |
| Title: | Odometric system for robots based on laser mice | |
| Description: | We developed an odometric system for robots by combining the reading of several laser mice. The system consists of a master PIC-based board and several slave boards where the sensors employed in optical mice are located. The readings are collected on the PIC and sent on the serial port to a PC which elaborates and combines the x and y readings in order to obtain a x,y,theta estimation of the movement of the robot.
The aim of the project is first to improve the current design of the PIC-based board, and realize a new working prototype, and then to implement and evaluate different algorithms able to estimate more precisely the x,y and theta odometric data from the mice readings. Experience with PIC-based systems and some experience with electronics circuits is a plus. Students are supposed to redesign the electronic board, improve the firmware of the PIC, and work on the algorithm that estimates the robot position on the PC. It would be also interesting to evaluate the possibility to embed the optimization and estimation algorithms in the firmware of the PIC in order to produce a stand-alone device. Ask the tutors of the project for extra material, such as data-sheets and other documentation. | |
| Tutor: | [[MatteoMatteucci | ]] (, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , … further resultswarning.png
| |
| Start: | 1 October 2009 | |
| Students: | 1 - 2 | |
| CFU: | 5 - 20 | |
| Research Area: | Robotics | |
| Research Topic: | Robot development | |
| Level: | Master of Science | |
| Type: | Course, Thesis |
| Wiki Page: | R2P IMU firmware development | |
| Title: | Embedded Inertial Measurement Unit for Unmanned Aerial Vehihcles | |
| Description: | We have developed the electronics of an Inertial Measurement Unit based on an ARM microcontroller to be integrated on an autonomous embedded aerial platform. The IMU has already some attitude heading reference system (AHRS) code implemented, but we are interested in:
Material
Expected outcome:
Required skills or skills to be acquired:
| |
| Tutor: | [[AndreaBonarini | ]] (, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , … further resultswarning.png
| |
| Start: | 1 January 2015 | |
| Students: | 1 - 2 | |
| CFU: | 2 - 20 | |
| Research Area: | Robotics | |
| Research Topic: | Robot development | |
| Level: | Bachelor of Science, Master of Science | |
| Type: | Course, Thesis |
| Wiki Page: | Scripting language on embedded platforms | |
| Title: | Scripting language on embedded platforms | |
| Description: | JOINT PROJECT with the Embedded Systems group (contact: Patrick Bellasi http://home.dei.polimi.it/bellasi/)
When developing embedded applications it is common the need to test some algorithm in some fast way, without to re-program the whole firmware every time. PAWN (http://www.compuphase.com/pawn/) is a *simple and lightweight scripting language with a C-like syntax*. Execution speed, stability, simplicity and a small footprint were essential design criteria for both the language and the abstract machine, making PAWN suitable for embedded applications. This project aims to port the abstract machine to ARM Cortex-M3 microcontrollers, add a set of functions to interface with the underlying hardware peripherals and then to embed it as ChibiOS/RT (http://www.chibios.org) thread. | |
| Tutor: | [[AndreaBonarini | ]] (, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , … further resultswarning.png
| |
| Start: | 30 May 2011 | |
| Students: | 1 - 2 | |
| CFU: | 2 - 5 | |
| Research Area: | Robotics | |
| Research Topic: | Robot development | |
| Level: | Bachelor of Science, Master of Science | |
| Type: | Course |
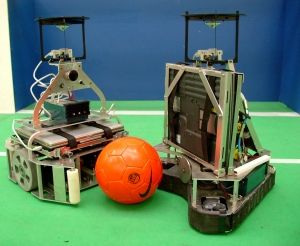
| Wiki Page: | Soccer Robots | |
| Title: | Soccer Robots | |
| Description: | Projects are available in different areas:
The project can be turned into a thesis by facing different problems in depth. | |
| Tutor: | [[MarcelloRestelli | ]] (, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , … further resultswarning.png
| |
| Start: | 1 January 2009 | |
| Students: | 1 - 2 | |
| CFU: | 5 - 20 | |
| Research Area: | Robotics | |
| Research Topic: | Robot development | |
| Level: | Bachelor of Science, Master of Science | |
| Type: | Course, Thesis |
| Wiki Page: | Stability and motion control of a balancing robot | |
| Title: | Stability and motion control of a balancing robot | |
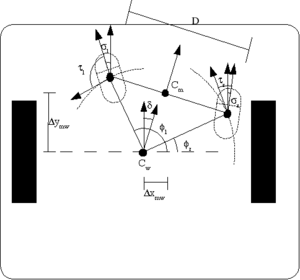
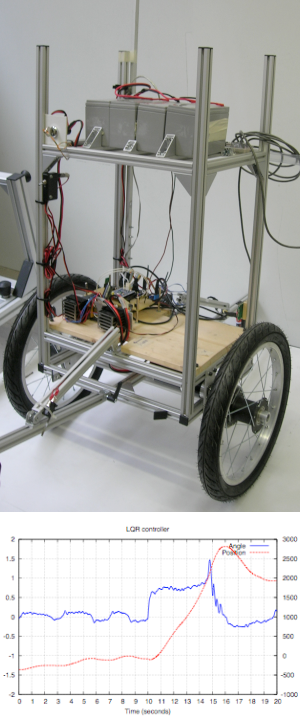
| Description: | This project is focused on the control of both stability and motion of TiltOne, a balancing robot.
TiltOne is a robot with only two wheels that can stand in vertical position following an unstable equilibrium point. The control is applied by commanding an amount of torque to the wheels, allowing the robot to mantain it's gravity center vertical aligned to the wheel axis. The aim of the project proposal is to implement and compare different control solutions, based on classical approach (as PID and LQR control) and Machine Learning approach (as Reinforcement Learning control policies), that allow the robot to move following a given trajectory at a given speed. | |
| Tutor: | [[AndreaBonarini | ]] (, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , … further resultswarning.png
| |
| Start: | 1 March 2010 | |
| Students: | 1 - 2 | |
| CFU: | 5 - 20 | |
| Research Area: | Robotics | |
| Research Topic: | Robot development | |
| Level: | Master of Science | |
| Type: | Course, Thesis |