User:MatteoMatteucci
Matteo Matteucci
| |
| E-Mail: | matteucc@elet.polimi.it |
| Research Areas: | |
This is my home page on the airwiki website. Here you can find projects and thesis proposals. You will not find here my research statements, my teaching material, my publications, and so on. If you are looking for something is not here you can try:
- My Personal home page (more complete and updated)
- My page at DEI (official home page)
Contents
PhD Students I am currently tutoring
- AndreaSemprebon
- BernardoDalSeno
- DavideCucci
- DavideMigliore
- FrancescoVisin
- LuigiMalago
- MarcoCannici
- RossellaBlatt
- SimoneCeriani
- SimoneMentasti
PhD Students I have tutored
Projects I am currently tutoring
- AGW (Control system design of an electric wheelchair for autonomous drive with obstacle avoidance MauroGabellone EugenioCeravolo)
- Deep Learning on Event-Based Cameras (This project aims to study deep learning techniques on event-based cameras and develop algorithms to perform object recognition on those devices. MarcoCannici)
- DiffDrivePlanner (A Search-Based Trajectory Planner for differential drive vehicles in ROS Context VitoRessa)
- HRVCar (DarioSortino FrancescoTogninalli Bruno Romano)
- I.DRIVE Data Logger (This project concerns the logging of data coming from multiple sensor installed in a car. This data are used to analyze the behaviours and the reactions of the driver AlessandroGabrielli)
- Low-cost IMU (Characterization of a low-cost IMU module developed by AIRLab; use of such module to extract high-level information about human behavior. NguyenHo)
- Object Recognition with Deep Boltzmann Machines (Deep Boltzmann machines for classification tasks CarloDEramo)
- RoboCom+R2P (The goal of the project is to develop a Robot equipped with collision avoidance logic. ValerioArcerito PietroBalatti AlessandroCianferotti)
- SLDR (LorenzoPorro)
- Sensor fusion for autonomous cars (This project concerns the logging and use of the data fusion coming from multiple sensor installed in a car. The data are used to generate the decisions and behavior of an autonomous car. LuisSierra)
- Sound source localization for robots (SimonePradolini)
- SprayinWithBrain (AI and Robotics in agriculture LorenzoFedeli Simone1Parisi LuigiBonoBonacchi)
- Triskar+R2P (The goal of the project is to build an omnidirectional robot based on existing hardware. AndreaCavalli LucaAgostini)
List of project proposals
| Wiki Page: | Accurate AR Marker Location | |
| Title: | C++ Library for accurate marker location based on subsequent pnp refinements | |
| Description: | ARTags, QR codes, Data Matrix, are visual landmark used for augmented reality, but they could be used for robotics as well. A thesis has already been done on using data matrix for robot localization and mapping, but improvements are required in terms generality, accuracy and robustness of the solution. The goal is thuss to:
Material:
Expected outcome:
Required skills or skills to be acquired:
| |
| Tutor: | [[MatteoMatteucci | ]] (, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , … further resultswarning.png
| |
| Start: | 1 January 2015 | |
| Students: | 1 - 2 | |
| CFU: | 5 - 10 | |
| Research Area: | Computer Vision and Image Analysis | |
| Research Topic: | None | |
| Level: | Bachelor of Science, Master of Science | |
| Type: | Thesis, Course |
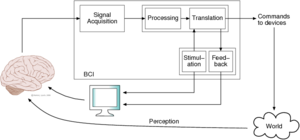
| Wiki Page: | Aperiodic visual stimulation in a VEP-based BCI | |
| Title: | Aperiodic visual stimulation in a VEP-based BCI | |
| Description: | Visual-evoked potentials (VEPs) are a possible way to drive the a Brain-Computer Interface (BCI). This projects aims at maximizing the discrimination between different stimuli by using numerical codes derived from techniques of digital telecommunications.
| |
| Tutor: | [[MatteoMatteucci | ]] (, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , … further resultswarning.png
| |
| Start: | 1 October 2009 | |
| Students: | 1 | |
| CFU: | 5 | |
| Research Area: | BioSignal Analysis | |
| Research Topic: | Brain-Computer Interface | |
| Level: | Bachelor of Science | |
| Type: | Course, Thesis |
| Wiki Page: | Automatic Differentiation Techniques for Real Time Kalman Filtering | |
| Title: | Evaluation of Automatic Differentiation Techniques for Gauss-Newton based Simultaneous Localization and Mapping | |
| Description: | In Gauss-Newton non linear optimization one of the most tedious part is computing Jacobians. At the AIRLab we have developed a framework for non linear Simultaneous Localization and Mapping suitable for different motion models and measurement equations, but any time you need to change something you need to recompute the required Jacobian. Automatic differentiation is a tool for the automatic differentiation of source code either at compiling time or at runtime; we are interested in testing these techniques in the software we have developed and compare their performance with respect to (cumbersome) optimized computation.
Material
Expected outcome: New modules implementations based on automatic differentiation A comparison between the old stuff and new approach Required skills or skills to be acquired:
| |
| Tutor: | [[MatteoMatteucci | ]] (, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , … further resultswarning.png
| |
| Start: | 1 January 2015 | |
| Students: | 1 - 2 | |
| CFU: | 10 - 20 | |
| Research Area: | Robotics | |
| Research Topic: | None | |
| Level: | Master of Science | |
| Type: | Thesis |
| Wiki Page: | Automatic generation of domain ontologies | |
| Title: | Automatic generation of domain ontologies | |
| Description: | This thesis to be developed together with Noustat S.r.l. (see http://www.noustat.it), who are developing research activities directed toward the optimization of knowledge management services, in collaboration with another company operating in this field. This project is aimed at removing the ontology building bottleneck, long and expensive activity that usually requires the direct collaboration of a domain expert. The possibility of automatic building the ontology, starting from a set of textual documents related to a specific domain, is expected to improve the ability to provide the knowledge management service, both by reducing the time-to-application, and by increasing the number of domains that can be covered. For this project, unsupervised learning methods will be applied in sequence, exploiting the topological properties of the ultra-metric spaces that emerge from the taxonomic structure of the concepts present in the texts, and associative methods will extend the concept network to lateral, non-hierarchical relationships. | |
| Tutor: | [[MatteoMatteucci | ]] (, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , … further resultswarning.png
| |
| Start: | ||
| Students: | 1 - 2 | |
| CFU: | 20 - 20 | |
| Research Area: | Machine Learning | |
| Level: | Master of Science | |
| Type: | Thesis |
| Wiki Page: | Behavior recognition from visual data | |
| Title: | Behavior recognition from visual data | |
| Description: | In the literature several approaches have been used to model observed behaviors and these date back to early approaches in animal behavior analysis (Baum and Eagon, 1967)(Colgan, 1978). Nowadays several techniques are used and they can be roughly classified as: State space models, Automata (e.g., Finite State Machines, Agents, etc.), Grammars (e.g., strings, T-Patterns, etc.), Bayeasian models (e.g., Hidden Markov Models), and Dynamic State Variables. The work will leverage on a huge corpus of techniques to devise the most suitable for behavior recognition from visual data. We exclude from the very beginning any deterministic approach being the phenomenon under observation complex and affected by noisy observations. The focus will be mainly of the use of dynamic graphical models (Ghahramani, 1998) and the application of bottom up learning techniques (Stolcke and Omohundro, 1993)(Stolcke and Omohundro, 1994) for model induction.
Material:
Expected outcome:
Required skills or skills to be acquired:
| |
| Tutor: | [[MatteoMatteucci | ]] (, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , … further resultswarning.png
| |
| Start: | 1 April 2012 | |
| Students: | 1 - 2 | |
| CFU: | 20 - 20 | |
| Research Area: | Machine Learning | |
| Research Topic: | None | |
| Level: | Master of Science | |
| Type: | Thesis |
| Wiki Page: | Combinatorial optimization based on stochastic relaxation | |
| Title: | Combinatorial optimization based on stochastic relaxation | |
| Description: | The project will focus on the study, implementation, comparison and
analysis of different algorithms for the optimization of pseudo-Boolean functions, i.e., functions defined over binary variables with values in R. These functions have been studied a lot in the mathematical programming literature, and different algorithms have been proposed (1). More recently, the same problems have been faced in evolutionary computations, with the use of genetic algorithms, and in particular estimation of distribution algorithms (2,3). Estimation of distribution algorithms are a recent meta-heuristic, where classical crossover and mutation operators used in genetic algorithms are replaced with operators that come from statistics, such as sampling and estimation. The focus will be on the implementation of a new algorithm able to combine different approaches (estimation and sampling, from one side, and exploitation of prior knowledge about the structure of problem, on the other), together with the comparison of the results with existing techniques that historically appear in different (and often separated) communities. Good coding (C/C++) abilities are required. Since the approach will be based on statistical models, the student is supposed to be comfortable with notions that come from probability and statistics courses. The project could require some extra effort in order to build and consolidate some background in math, especially in Bayesian statistics and MCMC techniques, such as Gibbs and Metropolis samplers (4). The project can be extended to master thesis, according to interesting and novel directions of research that will emerge in the first part of the work. Possible ideas may concern the proposal of new algorithms able to learn existing dependencies among the variables in the function to be optimized, and exploit them in order to increase the probability to converge to the global optimum. Picture taken from http://www.ra.cs.uni-tuebingen.de/ Bibliography
| |
| Tutor: | [[MatteoMatteucci | ]] (, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , … further resultswarning.png
| |
| Start: | 1 October 2009 | |
| Students: | 1 - 2 | |
| CFU: | 5 - 20 | |
| Research Area: | Machine Learning | |
| Research Topic: | Information Geometry, Stochastic Optimization | |
| Level: | Master of Science | |
| Type: | Course, Thesis |
| Wiki Page: | Combining Estimation of Distribution Algorithms and other Evolutionary techniques for combinatorial optimization | |
| Title: | Combining Estimation of Distribution Algorithms and other Evolutionary techniques for combinatorial optimization | |
| Description: | The project will focus on the study, implementation, comparison and analysis of different algorithms for combinatorial optimization using techniques and algorithms proposed in Evolutionary Computation. In particular we are interested in the study of Estimation of Distribution Algorithms (1,2,3,4), a recent meta-heuristic, often presented as an evolution of Genetic Algorithms, where classical crossover and mutation operators, used in genetic algorithms, are replaced with operators that come from statistics, such as sampling and
estimation. The focus will be on the implementation of new hybrid algorithms able to combine estimation of distribution algorithms with different approaches available in the evolutionary computation literature, such as genetic algorithms and evolutionary strategies, together with other local search techniques. Good coding (C/C++) abilities are required. Some background in combinatorial optimization form the "Fondamenti di Ricerca Operativa" is desirable. The project could require some effort in order to build and consolidate some background in MCMC techniques, such as Gibbs and Metropolis samplers (4). The project could be extended to master thesis, according to interesting and novel directions of research that will emerge in the first part of the work. Computer vision provides a large number of optimization problems, such as new-view synthesis, image segmentation, panorama stitching and texture restoration, among the others, (6). One common approach in this context is based on the use of binary Markov Random Fields and on the formalization of the optimization problem as the minimum of an energy function expressed as a square-free polynomial, (5). We are interested in the proposal, comparison and evaluation of different Estimation of Distribution Algorithms for solving real world problems that appear in computer vision. Pictures taken from http://www.genetic-programming.org and (6) Bibliography
| |
| Tutor: | [[MatteoMatteucci | ]] (, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , … further resultswarning.png
| |
| Start: | 1 October 2009 | |
| Students: | 1 - 2 | |
| CFU: | 5 - 10 | |
| Research Area: | Machine Learning | |
| Research Topic: | Evolutionary Computation, Stochastic Optimization | |
| Level: | Master of Science | |
| Type: | Course, Thesis |
| Wiki Page: | Comparison of State of the Art Visual Odometry Systems | |
| Title: | A Comparison of State of the Art Visual Odometry Systems (Monocular and Stereo) | |
| Description: | Visual odometry is the estimation of camera(s) movement from a sequence of images. In case we deal with a single camera system we have Monocular Visual Odometry; in case we have more cameras we have a Stero Visual Odometry. The goal of the thesis is to review the state of the art on in visual odometry, classify existing approaches and compare their implementations (many of the algorithms have online source code available).
Material
Expected outcome:
Required skills or skills to be acquired:
| |
| Tutor: | [[MatteoMatteucci | ]] (, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , … further resultswarning.png
| |
| Start: | 1 January 2015 | |
| Students: | 1 - 2 | |
| CFU: | 10 - 20 | |
| Research Area: | Computer Vision and Image Analysis | |
| Research Topic: | None | |
| Level: | Bachelor of Science, Master of Science | |
| Type: | Thesis, Course |
| Wiki Page: | Creation of new EEG training by introduction of noise | |
| Title: | Creation of new EEG training by introduction of noise | |
| Description: | A Brain-Computer Interface (BCI) must be trained on the individual user in order to be effective. This training phase require recording data in long sessions, which is time consuming and boring for the user. The aim of this project is to develop algorithm to create new training EEG (electroencephalography) data from existing ones, so as to speed up the training phase.
| |
| Tutor: | [[MatteoMatteucci | ]] (, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , … further resultswarning.png
| |
| Start: | 1 October 2009 | |
| Students: | 1 - 2 | |
| CFU: | 5 - 20 | |
| Research Area: | BioSignal Analysis | |
| Research Topic: | Brain-Computer Interface | |
| Level: | Bachelor of Science, Master of Science | |
| Type: | Course, Thesis |
| Wiki Page: | Driving an autonomous wheelchair with a P300-based BCI | |
| Title: | Driving an autonomous wheelchair with a P300-based BCI | |
| Description: | This project pulls together different Airlab projects with the aim to drive an autonomous wheelchair (LURCH) with a BCI, through the development of key software modules. Depending on the effort the student is willing to put into it, the project can grow to a full experimental thesis. | |
| Tutor: | [[MatteoMatteucci | ]] (, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , … further resultswarning.png
| |
| Start: | 1 November 2008 | |
| Students: | 1 | |
| CFU: | 5 - 20 | |
| Research Area: | BioSignal Analysis | |
| Research Topic: | Brain-Computer Interface | |
| Level: | Bachelor of Science, Master of Science | |
| Type: | Course |
| Wiki Page: | Environment Monitoring | |
| Title: | Environment Monitoring | |
| Description: | The goal of this project is to develop a video surveillance system to track in 3D vehicles or people.
The idea is to use one or more calibrated camera to estimate the position and the trajectories of the moving objects in the scene. The skills required for this project are:
| |
| Tutor: | [[MatteoMatteucci | ]] (, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , … further resultswarning.png
| |
| Start: | ||
| Students: | 2 - 3 | |
| CFU: | 10 - 15 | |
| Research Area: | Computer Vision and Image Analysis | |
| Type: | Course |
| Wiki Page: | Exploratory data analysis by genetic feature extraction | |
| Title: | Exploratory data analysis by genetic feature extraction | |
| Description: | Understanding the waves in EEG signals is an hard task and psicologists often need automatic tools to perform this task. In this project we are interested in using a genetic algorithm developed for P300 feature extraction in order to extract useful informations from Error Potentials. The project is a collaboration with the psicology department od Padua University.
| |
| Tutor: | [[MatteoMatteucci | ]] (, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , … further resultswarning.png
| |
| Start: | 1 October 2009 | |
| Students: | 1 - 2 | |
| CFU: | 5 - 20 | |
| Research Area: | BioSignal Analysis | |
| Research Topic: | Brain-Computer Interface | |
| Level: | Master of Science | |
| Type: | Course, Thesis |
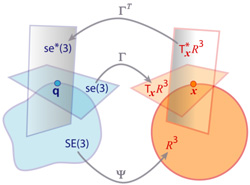
| Wiki Page: | Extended Kalman Filtering on Manifolds | |
| Title: | Extended Kalman Filtering on Manifolds | |
| Description: | Extended Kalman filtering is a well known technique for the estimation of the state of a dynamical system also used in robotics for localization and mapping. However in the basic formulation it assumes all variables to live in an Euclidean space while some components may span over the non-Euclidean 2D or 3D rotation group SO(2) or SO(3). It is thus possible to write tha Extended Kalman filter to operate on Lie Groups to take into account the presence of manifolds (http://www.ethaneade.org/latex2html/lie/lie.html). We are interestend in investigation this further applying it to the EKF-SLAM framework we have developed.
Material:
Expected outcome:
Required skills or skills to be acquired:
| |
| Tutor: | [[MatteoMatteucci | ]] (, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , … further resultswarning.png
| |
| Start: | 1 April 2012 | |
| Students: | 1 - 2 | |
| CFU: | 20 - 20 | |
| Research Area: | Robotics | |
| Research Topic: | None | |
| Level: | Master of Science | |
| Type: | Thesis |
| Wiki Page: | Information geometry and machine learning | |
| Title: | Information geometry and machine learning | |
| Description: | In machine learning, we often introduce probabilistic models to handle uncertainty in the data, and most of the times due to the computational cost, we end up selecting (a priori, or even at run time) a subset of all possible statistical models for the variables that appear in the problem. From a geometrical point of view, we work with a subset (of points) of all possible statistical models, and the choice of the fittest model in out subset can be interpreted as a the point (distribution) minimizing some distance or divergence function w.r.t. the true distribution from which the observed data are sampled. From this perspective, for instance, estimation procedures can be considered as projections on the statistical model and other statistical properties of the model can be understood in geometrical terms. Information Geometry (1,2) can be described as the study of statistical properties of families of probability distributions, i.e., statistical models, by means of differential and Riemannian geometry.
Information Geometry has been recently applied in different fields, both to provide a geometrical interpretation of existing algorithms, and more recently, in some contexts, to propose new techniques to generalize or improve existing approaches. Once the student is familiar with the theory of Information Geometry, the aim of the project is to apply these notions to existing machine learning algorithms. Possible ideas are the study of a particular model from the point of view of Information Geometry, for example as Hidden Markov Models, Dynamic Bayesian Networks, or Gaussian Processes, to understand if Information Geometry can give useful insights with such models. Other possible direction of research include the use of notions and ideas from Information Geometry, such as the mixed parametrization based on natural and expectation parameters (3) and/or families of divergence functions (2), in order to study model selection from a geometric perspective. For example by exploiting projections and other geometric quantities with "statistical meaning" in a statistical manifold in order to chose/build the model to use for inference purposes. Since the project has a theoretical flavor, mathematical inclined students are encouraged to apply. The project requires some extra effort in order to build and consolidate some background in math, partially in differential geometry, and especially in probability and statistics. Bibliography
| |
| Tutor: | [[MatteoMatteucci | ]] (, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , … further resultswarning.png
| |
| Start: | 1 October 2009 | |
| Students: | 1 - 2 | |
| CFU: | 20 - 20 | |
| Research Area: | Machine Learning | |
| Research Topic: | Information Geometry | |
| Level: | Master of Science | |
| Type: | Course, Thesis |
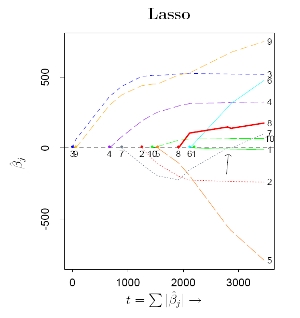
| Wiki Page: | LARS and LASSO in non Euclidean Spaces | |
| Title: | LARS and LASSO in non Euclidean Spaces | |
| Description: | LASSO (1) and more recently LARS (2) are two algorithms proposed for linear regression tasks. In particular LASSO solves a least-squares (quadratic) optimization problem with a constrain that limits the sum of the absolute value of the coefficients of the regression, while LARS can be considered as a generalization of LASSO, that provides a more computational efficient way to obtain the solution of the regression problem simultaneously for all values of the constraint introduced by LASSO.
One of the common hypothesis in regression analysis is that the noise introduced in order to model the linear relationship between regressors and dependent variable has a Gaussian distribution. A generalization of this hypothesis leads to a more general framework, where the geometry of the regression task is no more Euclidean. In this context different estimation criteria, such as maximum likelihood estimation and other canonical divergence functions do not coincide anymore. The target of the project is to compare the different solutions associated to different criteria, for example in terms of robustness, and propose generalization of LASSO and LARS in non Euclidean contexts. The project will focus on the understanding of the problem and on the implementation of different algorithms, so (C/C++ or Matlab or R) coding will be required. Since the project has also a theoretical flavor, mathematical inclined students are encouraged to apply. The project may require some extra effort in order to build and consolidate some background in math, especially in probability and statistics. Picture taken from (2) Bibliography
| |
| Tutor: | [[MatteoMatteucci | ]] (, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , … further resultswarning.png
| |
| Start: | 1 October 2009 | |
| Students: | 1 - 2 | |
| CFU: | 20 - 20 | |
| Research Area: | Machine Learning | |
| Research Topic: | Informtion Geometry | |
| Level: | Master of Science | |
| Type: | Course, Thesis |
| Wiki Page: | MoonSLAM Reengineering | |
| Title: | Reengineering of a flexible framework for simultaneous localization and mapping | |
| Description: | In the last three years a general framework for the implementation of EKF-SLAM algorithm has been developed at the AIRLab. After several improvements it is now time to redesign it based on the experience cumulated. The goal is to have an international reference framework for the development of EKF based SLAM algorithms with multiple sensors (e.g., lasers, odometers, inertial measurement ) and different motion models (e.g., free 6DoF motion, planar motion, ackerman kinematic, and do on). The basic idea is to implement it by using C++ templates, numerically stable techniques for Kalman filtering and investigation the use of automatic differentiation. It should be possible to seamlessly exchange motion model and sensor model without having to write code beside the motion model and the measurement equation.
Material
Expected outcome:
Required skills:
| |
| Tutor: | [[MatteoMatteucci | ]] (, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , … further resultswarning.png
| |
| Start: | 1 January 2015 | |
| Students: | 1 - 2 | |
| CFU: | 20 - 20 | |
| Research Area: | Robotics | |
| Research Topic: | None | |
| Level: | Master of Science | |
| Type: | Thesis |
| Wiki Page: | Multimodal GUI for driving an autonomous wheelchair | |
| Title: | Multimodal GUI for driving an autonomous wheelchair | |
| Description: | This project pulls together different Airlab projects with the aim to drive an autonomous wheelchair (LURCH - The autonomous wheelchair) with a multi modal interface (Speech Recognition, Brain-Computer Interface, etc.), through the development of key software modules. The work will be validated with live experiments.
| |
| Tutor: | [[MatteoMatteucci | ]] (, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , … further resultswarning.png
| |
| Start: | 1 October 2009 | |
| Students: | 1 - 2 | |
| CFU: | 5 - 10 | |
| Research Area: | BioSignal Analysis | |
| Research Topic: | Brain-Computer Interface | |
| Level: | Bachelor of Science, Master of Science | |
| Type: | Course |
| Wiki Page: | Odometric system for robots based on laser mice | |
| Title: | Odometric system for robots based on laser mice | |
| Description: | We developed an odometric system for robots by combining the reading of several laser mice. The system consists of a master PIC-based board and several slave boards where the sensors employed in optical mice are located. The readings are collected on the PIC and sent on the serial port to a PC which elaborates and combines the x and y readings in order to obtain a x,y,theta estimation of the movement of the robot.
The aim of the project is first to improve the current design of the PIC-based board, and realize a new working prototype, and then to implement and evaluate different algorithms able to estimate more precisely the x,y and theta odometric data from the mice readings. Experience with PIC-based systems and some experience with electronics circuits is a plus. Students are supposed to redesign the electronic board, improve the firmware of the PIC, and work on the algorithm that estimates the robot position on the PC. It would be also interesting to evaluate the possibility to embed the optimization and estimation algorithms in the firmware of the PIC in order to produce a stand-alone device. Ask the tutors of the project for extra material, such as data-sheets and other documentation. | |
| Tutor: | [[MatteoMatteucci | ]] (, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , … further resultswarning.png
| |
| Start: | 1 October 2009 | |
| Students: | 1 - 2 | |
| CFU: | 5 - 20 | |
| Research Area: | Robotics | |
| Research Topic: | Robot development | |
| Level: | Master of Science | |
| Type: | Course, Thesis |
| Wiki Page: | P300 BCI | |
| Title: | P300 BCI for ALS patient | |
| Description: | Recovery, integration and adaptation of P300 BCI (hardware and software) stubs to generate a working interface for a speller. The aim is to develop a working prototype for an ALS affected patient. | |
| Tutor: | [[MatteoMatteucci | ]] (, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , … further resultswarning.png
| |
| Start: | 1 April 2011 | |
| Students: | 1 - 3 | |
| CFU: | 2 - 20 | |
| Research Area: | BioSignal Analysis | |
| Research Topic: | EEG analysis, classification algorithms | |
| Level: | Master of Science, PhD | |
| Type: | Thesis |
| Wiki Page: | Poit cloud SLAM with Microsoft Kinect | |
| Title: | Point cloud SLAM with Microsoft Kinect | |
| Description: | Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) is one of the basic functionalities required from an autonomous robot. In the past we have developed a framework for building SLAM algorithm based on the use of the Extended Kalman Filter and vision sensors. A recently available vision sensor which has tremendous potential for autonomous robots is the Microsoft Kinect RGB-D sensor. The thesis aims at the integration of the Kinect sensor in the framework developed for the development of a point cloud base system for SLAM.
Material:
Expected outcome:
Required skills or skills to be acquired:
| |
| Tutor: | [[MatteoMatteucci | ]] (, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , … further resultswarning.png
| |
| Start: | 1 January 2015 | |
| Students: | 1 - 2 | |
| CFU: | 10 - 20 | |
| Research Area: | Computer Vision and Image Analysis | |
| Research Topic: | None | |
| Level: | Master of Science | |
| Type: | Thesis |
… further results
Past project proposals
- Aperiodic visual stimulation in a VEP-based BCI (Visual-evoked potentials (VEPs) are a possible way to drive the a Brain-Computer Interface (BCI). This projects aims at maximizing the discrimination between different stimuli by using numerical codes derived from techniques of digital telecommunications.
- J.R. Wolpaw et al. Brain-computer interfaces for communication and control (http://tinyurl.com/yhq27pq)
- Erich E. Sutter. The brain response interface: communication through visually-induced electrical brain responses (http://tinyurl.com/yfqvwp6))
- L. E. Baum and J. A. Eagon. An inequality with applications to statistical estimation for probabilistic functions of markov processes and to a model for ecology. Bull. Amer. Math. Soc, 73(73):360–363, 1967.
- P. W. Colgan. Quantitative Ethology. John Wiley & Sons, New York, 1978.
- A. Stolcke and S. M. Omohundro. Hidden markov model induction by bayesian model merging. In Stephen Jos é Hanson, Jack D. Cowan, and C. Lee Giles, editors, Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, volume 5. Morgan Kaufmann, San Mateo, CA, 1993.
- Zoubin Ghahramani. Learning dynamic bayesian networks. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, 1387:168, 1998.
- A. Stolcke and S. M. Omohundro. Best-first model merging for hidden markov model induction. Technical Report TR-94-003, 1947 Center Street, Berkeley, CA, 1994.
- papers from major journals and conferences
- kinet SDK for the extraction of body poses
- general framework for the recognition of behaviors from time series
- toolkit for behavior segmentation and recognition from time series
- running prototype based on data coming from the Microsoft kinect sensor
- understanding of techniques for behavior recognition
- background on pattern recognition and stochastic models
- basic understanding of computer vision
- C++ programming under Linux or Matlab)
- Boros, Endre and Boros, Endre and Hammer, Peter L. (2002) Pseudo-boolean optimization. Discrete Applied Mathematics.
- Pelikan, Martin; Goldberg, David; Lobo, Fernando (1999), A Survey of Optimization by Building and Using Probabilistic Models, Illinois: Illinois Genetic Algorithms Laboratory (IlliGAL), University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign.
- Larrañga, Pedro; & Lozano, Jose A. (Eds.). Estimation of distribution algorithms: A new tool for evolutionary computation. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Boston, 2002.
- Image Analysis, Random Fields Markov Chain Monte Carlo Methods)
- Pelikan, Martin; Goldberg, David; Lobo, Fernando (1999), A Survey of Optimization by Building and Using Probabilistic Models, Illinois: Illinois Genetic Algorithms Laboratory (IlliGAL), University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign.
- Larrañga, Pedro; & Lozano, Jose A. (Eds.). Estimation of distribution algorithms: A new tool for evolutionary computation. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Boston, 2002.
- Lozano, J. A.; Larrañga, P.; Inza, I.; & Bengoetxea, E. (Eds.). Towards a new evolutionary computation. Advances in estimation of distribution algorithms. Springer, 2006.
- Pelikan, Martin; Sastry, Kumara; & Cantu-Paz, Erick (Eds.). Scalable optimization via probabilistic modeling: From algorithms to applications. Springer, 2006.
- Image Analysis, Random Fields Markov Chain Monte Carlo Methods
- Carsten Rother, Vladimir Kolmogorov, Victor Lempitsky, Martin Szummer. Optimizing Binary MRFs via Extended Roof Duality, CVPR 2007)
- J.R. Wolpaw et al. Brain-computer interfaces for communication and control (http://tinyurl.com/yhq27pq))
- B. Dal Seno, M. Matteucci, and L. Mainardi. "A genetic algorithm for automatic feature extraction in P300 detection" (http://home.dei.polimi.it/dalseno/papers/2008/ijcnn08.pdf)
- B. Dal Seno, M. Matteucci, L. Mainardi, F. Piccione, and S. Silvoni. "Single-trial P300 detection in healthy and ALS subjects by means of a genetic algorithm" (http://home.dei.polimi.it/dalseno/papers/2008/grazGa08.pdf))
- papers about Manifold based optimization and space representations
- C++ framework for EKF-SLAM
- An extended Kalman filter which uses this new representation
- Good mathematical background
- C++ programming under Linux)
- Shun-ichi Amari, Hiroshi Nagaoka, Methods of Information Geometry, 2000
- Shun-ichi Amari, Information geometry of its applications: Convex function and dually flat manifold, Emerging Trends in Visual Computing (Frank Nielsen, ed.), Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 5416, Springer, 2009, pp. 75–102
- Shun-ichi Amari, Information geometry on hierarchy of probability distributions, IEEE Transactions on Information Theory 47 (2001), no. 5, 1701–1711.)
- Tibshirani, R. (1996), Regression shrinkage and selection via the lasso. J. Royal. Statist. Soc B., Vol. 58, No. 1, pages 267-288
- Bradley Efron, Trevor Hastie, Iain Johnstone and Robert Tibshirani, Least Angle Regression, 2003)
- R. Blatt et al. Brain Control of a Smart Wheelchair (http://tinyurl.com/ygldwun))
- implementing embedded algorithms for the estimation of the IMU attitude to be compared with the actual one (e.g., Kalman filter, DCM, Madgwick, etc.)
- developing a, easy to use, procedure for the calibration of IMU parameters
- making a comparison with commercial units using a robot arm as testbed
- validate the accuracy of the IMU on a flying platform
- integrate the measurements from a GPS to reduce drift and provide accurate positiong (this will make it definitely a MS thesis)
- electronic board and eclipse based C development toolkit for ARM processors
- papers describing the algorithms we are interested in implementing
- few different AHRS algorithms with comparative results
- user-friendly procedure to calibrate the IMU
- a sistem which integrated IMU and GPS to provide accurate positioning
- C programming on ARM microcontroller
- background on kalman filtering and attitude estimation)
- J.R. Wolpaw et al. Brain-computer interfaces for communication and control (http://tinyurl.com/yhq27pq)
- R.J. Croff, R.J. Barry. Removal of ocular artifact from the EEG: a review (http://tinyurl.com/ykk6ks9))
- A framework for multisensor SLAM using the world centric approach
- Papers and report about robocentric slam
- a fully functional robocentric version of the MoonSLAM framework
- Basic background in computer vision
- Background in Kalman filtering
- C++ programming under Linux)
- a MS thesis which describes the scan matching algorithms
- a BS thesis which implements a prototype of the system
- a complete system that build maps integrating laser scan and visual informtion
- Background on Kalman filtering
- C++ programming under Linux)
- datasets with real data
- a few odometric system implementations
- C++ libraries for non linear optimization
- software for the self calibration of a set of odometry systems mounted on the same robot
- C++ programming under Linux)
- Felsenstein 2003: Inferring Phylogenies
- Semple and Steel 2003: Phylogenetics: The mathematics of phylogenetics
- Louis J. Billera, Susan P. Holmes and and Karen Vogtmann Geometry of the space of phylogenetic trees. Advances in Applied Math 27, 733-767 (2001)
- Evans, S.N. and Speed, T.P. (1993). Invariants of some probability models used in phylogenetic inference. Annals of Statistics 21, 355-377.
- Lior Pachter, Bernd Sturmfels 2005, Algebraic Statistics for Computational Biology.
- A. Walenstein, E-Md. Karim, A. Lakhotia, and L. Parida. Malware Phylogeny Generation Using Permutations of Code, Journal in Computer Virology, v1.1, 2005.)
Past tutored projects
- BCI & artifacts (DarioRusignuolo)
- BCI based on Motor Imagery (FabioZennaro)
- BCI on Sockets (MarioPolino NikoZarzani)
- Balancing Robot Development (MattiaCrippa MarcoLattarulo MichelePersiani)
- Characterization of the NIA signal (GiulioValenti)
- Extraction (FabioMarfia)
- Gestures in Videogames (GiorgioPrini)
- HeadsetControlForWheelChair (RobertoVandone)
- Indoor localization system based on a gyro and visual passive markers (DarioCecchetto LorenzoConsolaro)
- Integration of scanSLAM and ARToolKit in the MoonSLAM framework (MatteoLuperto MladenMazuran)
- Interpretation of facial expressions and movements of the head (CristianMandelli)
- Machine Learning for Crop Weed Classification (LodewijkVoorhoeve)
- R2P (AndreaZoppi)
- Recognition of the user's focusing on the stimulation matrix (LeonardoVolpe)
- Robot Localization and Navigation With Visual Markers (AndreaPremarini AndreaScalise)
- Stimulus tagging using aperiodic visual stimulation in a VEP-based BCI (DavideCastellone GiuseppeBroccio)
- Triskar (AndreaSorbelli AlessandroDeangelis)
Past tutored students
- AlfredoMotta
- AndreaCampana
- AndreaPremarini
- AndreaScalise
- AndreaSgarlata
- AndreaSorbelli
- AntonioTripodi
- BernardoDalSeno
- ClaudioSesto
- DanielaMazzeo
- DarioCecchetto
- DarioRusignuolo
- DavideCastellone
- DavideCucci
- DavideMigliore
- DiegoConsolaro
- EleonoraCiceri
- EmanueleCorsano
- ErmesViviani
- FabioBeltramini
- … further results